Hi everyone,
I’ve been working on a integration for Snooz white noise machines with Hubitat.
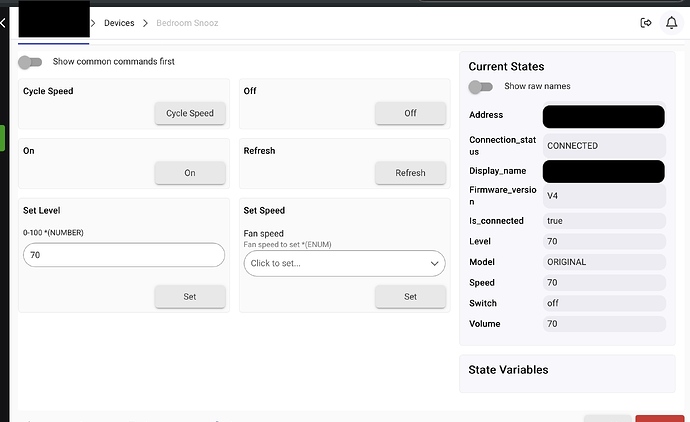
The goal was to get reliable on/off + volume control inside Hubitat. The approach is a small BLE-backed WebSocket service(runs on a Linux device like a Raspberry Pi, or even a Mac) plus Hubitat parent/child drivers that maintain a persistent WS connection and create a child device per Snooz unit.
![]() KEY FEATURES:
KEY FEATURES:
 Local-only control over Bluetooth (no cloud)
Local-only control over Bluetooth (no cloud) Persistent WebSocket & Bluetooth connection from Hubitat → BLE service (LAN)
Persistent WebSocket & Bluetooth connection from Hubitat → BLE service (LAN) Multi-device support (one BLE host, multiple Snooz devices)
Multi-device support (one BLE host, multiple Snooz devices) Child device per Snooz machine with:
Child device per Snooz machine with:
- Switch (on/off)
- Volume (0–100)
- Exposed as a Fan device (speed maps to volume) for Homebridge friendliness
- Connection metadata (connected / model / firmware / etc.)
 Optional Bearer token auth on the WebSocket service
Optional Bearer token auth on the WebSocket service Docker / docker-compose ready service for easy deployment
Docker / docker-compose ready service for easy deployment macOS support (on Mac you typically match by device name instead of address)
macOS support (on Mac you typically match by device name instead of address)
![]() How it works (high level):
How it works (high level):
- A BLE host (Pi / Linux box / etc.) runs the Python WS service
- The service talks to Snooz devices over Bluetooth using pysnooz
- Hubitat connects over WebSocket and auto-creates child devices
- Commands flow Hubitat → WS → BLE and state updates flow back WS → Hubitat
![]() GitHub Repo & Setup Guide:
GitHub Repo & Setup Guide:
https://github.com/K-MTG/Hubitat-Snooz-BLE
![]() My hardware setup so far:
My hardware setup so far:
- Tested on Raspberry Pi (Ubuntu Server) & iMac
- BLE reliability improves a lot with a decent USB Bluetooth adapter if you’re in a noisy RF environment or farther away
![]() Notes / Tips:
Notes / Tips:
- This is LAN-local only — don’t expose the WS port (8765) to the internet.
- If your LAN has untrusted devices, enable the auth token.
- On macOS, BLE “addresses” can show up as UUIDs — the service supports matching by device name (e.g.
Snooz-040F) which works better.
Feedback, issues, and suggestions are very welcome!